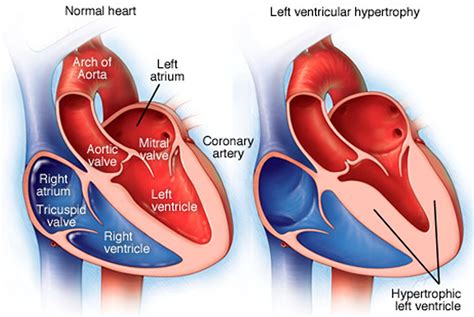
lv enlargement radiopaedia | normal left ventricular enlargement lv enlargement radiopaedia Left ventricular enlargement can be reliably identified on nongated contrast-enhanced multidetector CT when the maximum luminal diameter of the LV is greater than 5.6 cm. . $18K+
0 · normal left ventricular enlargement
1 · left ventricular enlargement ultrasound
2 · left ventricular enlargement radiology
3 · left ventricular enlargement pictures
4 · left ventricular enlargement morphology
5 · left ventricular enlargement ct
6 · elevated left ventricular volume x ray
7 · echocardiogram left ventricular enlargement
Pre-owned Rolex Submariner ref 116613 (2009) is a desirable edition of the modern Rolex "Bluesy" because it predates the release of the "Sunburst" blue dial variant, which was .
normal left ventricular enlargement
lil debbie kreayshawn gucci gucci
The parasternal long axis and apical four-chamber views on transthoracic echocardiography are often the primary views used to gain both a qualitative and quantitative .Left atrial enlargement (LAE) may result from many conditions, either congenital .Left ventricular enlargement can be reliably identified on nongated contrast-enhanced multidetector CT when the maximum luminal diameter of the LV is greater than 5.6 cm. . Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) is generally considered to be an adaptive response that allows for normal ejection fraction despite abnormal pressure and/or volume .
LV enlargement (LVE) is associated with a wide variety of cardiovascular processes, including cardiomyopathy, myocardial infarction, valvular heart disease, PH, and .
LV mass assessed by echocardiography and CMR, cardiovascular outcomes, and medical practice. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging 2012 ;5(8):837–848. Medline Google Scholar Left ventricular hypertrophy was strongly associated with hard coronary heart disease events (death and myocardial infarction) over 15 years of follow-up in a contemporary . Radiological sign of left ventricular enlargement based on the distance between the inferior vena cava (IVC) and left ventricle (LV). Left ventricular enlargement is suggested on lateral chest radiograph if the . Left atrial enlargement (LAE) may result from many conditions, either congenital or acquired. It has some characteristic findings on a frontal chest radiograph. CT or MRI may .
Normal LV myocardial thickness is <11 mm. 5 LVH is considered mild if it measures 11-13 mm, moderate if it measures 14-15 mm, and severe if it measures >15 mm. LVH can .
The parasternal long axis and apical four-chamber views on transthoracic echocardiography are often the primary views used to gain both a qualitative and quantitative appreciation of left ventricular enlargement. Features include 4: increased left ventricular internal end-diastolic diameter (LVIDd)Left ventricular hypertrophy is a condition where the muscle wall of the heart's left pumping chamber thickens.Left ventricular enlargement can be reliably identified on nongated contrast-enhanced multidetector CT when the maximum luminal diameter of the LV is greater than 5.6 cm. Nongated contrast-enhanced CT scan can be used to recognize LVE.
left ventricular enlargement ultrasound
Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) is generally considered to be an adaptive response that allows for normal ejection fraction despite abnormal pressure and/or volume load. 1 However, this adaptation is associated with increased cardiac morbidity and mortality, including acute myocardial infarction, heart failure, arrhythmia, and stroke. 2–4 . LV enlargement (LVE) is associated with a wide variety of cardiovascular processes, including cardiomyopathy, myocardial infarction, valvular heart disease, PH, and congestive heart failure (25–28). LV mass assessed by echocardiography and CMR, cardiovascular outcomes, and medical practice. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging 2012 ;5(8):837–848. Medline Google Scholar Left ventricular hypertrophy was strongly associated with hard coronary heart disease events (death and myocardial infarction) over 15 years of follow-up in a contemporary ethnically diverse cohort, after adjustment for traditional risk factors and coronary artery calcium.
Radiological sign of left ventricular enlargement based on the distance between the inferior vena cava (IVC) and left ventricle (LV). Left ventricular enlargement is suggested on lateral chest radiograph if the distance (A) between the LV border border and the posterior border of IVC is more than 1.8 cm at a level 2 cm above the intersection of .
Left atrial enlargement (LAE) may result from many conditions, either congenital or acquired. It has some characteristic findings on a frontal chest radiograph. CT or MRI may also be used for diagnosis. Normal LV myocardial thickness is <11 mm. 5 LVH is considered mild if it measures 11-13 mm, moderate if it measures 14-15 mm, and severe if it measures >15 mm. LVH can also be defined and quantified in terms of absolute and BSA-indexed LV mass values, with values over the 95th percentile considered abnormal (91 g/m 2 in males and 77 g/m 2 in .
The parasternal long axis and apical four-chamber views on transthoracic echocardiography are often the primary views used to gain both a qualitative and quantitative appreciation of left ventricular enlargement. Features include 4: increased left ventricular internal end-diastolic diameter (LVIDd)Left ventricular hypertrophy is a condition where the muscle wall of the heart's left pumping chamber thickens.Left ventricular enlargement can be reliably identified on nongated contrast-enhanced multidetector CT when the maximum luminal diameter of the LV is greater than 5.6 cm. Nongated contrast-enhanced CT scan can be used to recognize LVE. Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) is generally considered to be an adaptive response that allows for normal ejection fraction despite abnormal pressure and/or volume load. 1 However, this adaptation is associated with increased cardiac morbidity and mortality, including acute myocardial infarction, heart failure, arrhythmia, and stroke. 2–4 .
LV enlargement (LVE) is associated with a wide variety of cardiovascular processes, including cardiomyopathy, myocardial infarction, valvular heart disease, PH, and congestive heart failure (25–28). LV mass assessed by echocardiography and CMR, cardiovascular outcomes, and medical practice. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging 2012 ;5(8):837–848. Medline Google Scholar
Left ventricular hypertrophy was strongly associated with hard coronary heart disease events (death and myocardial infarction) over 15 years of follow-up in a contemporary ethnically diverse cohort, after adjustment for traditional risk factors and coronary artery calcium. Radiological sign of left ventricular enlargement based on the distance between the inferior vena cava (IVC) and left ventricle (LV). Left ventricular enlargement is suggested on lateral chest radiograph if the distance (A) between the LV border border and the posterior border of IVC is more than 1.8 cm at a level 2 cm above the intersection of . Left atrial enlargement (LAE) may result from many conditions, either congenital or acquired. It has some characteristic findings on a frontal chest radiograph. CT or MRI may also be used for diagnosis.

$18K+
lv enlargement radiopaedia|normal left ventricular enlargement