lv wall motion abnormality | regional wall motion abnormalities present lv wall motion abnormality Regional wall motion abnormalities (WMAs) after myocardial infarction are associated with adverse remodeling and increased mortality in the short to medium term. Their . $132.64
0 · what is rwma in cardiology
1 · regional wall motion abnormalities present
2 · left ventricular wall segments echo
3 · left ventricular segmental wall motion
4 · echo regional wall motion abnormalities
5 · basal inferior wall is hypokinetic
6 · basal inferior wall hypokinesis
7 · abnormal left ventricular wall motion
COVID-19. ARRIVING AT MIA. DEPARTING FROM MIA. SECURITY & BORDER CONTROL. SECURITY SCREENING AREA / HAND LUGGAGE ALLOWANCES. .
Left ventricular wall motion abnormalities (LVWMAs) are commonly observed in a variety of medical conditions, including coronary artery disease, congestive heart failure, . Echocardiographic evaluation of wall motion (WM) is a simple, well-validated method to assess segmental left ventricular (LV) function. 1,2 The presence of qualitative WM . Regional wall motion abnormalities (WMAs) after myocardial infarction are associated with adverse remodeling and increased mortality in the short to medium term. Their .Assessment of left ventricular systolic function has a central role in the evaluation of cardiac disease. Accurate assessment is essential to guide management and prognosis. Numerous echocardiographic techniques are used in the .
There were 52 patients (5.9%) with echocardiographic evidence of LV wall motion abnormality. Frequency of LV wall motion abnormality did not differ between patients with .
Left Ventricular (LV) wall motion abnormalities (WMA) are an independent indicator of adverse cardiovascular events and death in patients with cardiovascular diseases such as myocardial . LBBB is known to cause septal wall motion abnormalities as well as to reduce systolic septal wall thickness. Thus, LBBB is a good non-ischaemic clinical model to evaluate .Abnormal ventricular wall motion is a strong clinical predictor of sudden, arrhythmic, cardiac death. Dispersion in repolarization is a prerequisite for the initiation of re-entrant arrhythmia. .The most frequent cause of regional wall motion abnormality is ischemic heart disease. Myocardial infarction may cause regional hypokinesia, akinesia or dyskinesia. The distribution of wall motion abnormalities should match the territory of a coronary artery.

Left ventricular hypertrophy is a thickening of the wall of the heart's main pumping chamber, called the left ventricle. This thickening may increase pressure within the heart. The condition can make it harder for the heart to pump blood. Left ventricular wall motion abnormalities (LVWMAs) are commonly observed in a variety of medical conditions, including coronary artery disease, congestive heart failure, stress-induced cardiomyopathy, myocarditis, chronic renal disease, and stroke. 1–4 Their underlying disease mechanisms and their potential causative role for stroke remain . Echocardiographic evaluation of wall motion (WM) is a simple, well-validated method to assess segmental left ventricular (LV) function. 1,2 The presence of qualitative WM abnormalities has been demonstrated to be an independent predictor of cardiovascular events in groups of patients with myocardial infarction (MI), 3,4 unstable angina, 5 . Regional wall motion abnormalities (WMAs) after myocardial infarction are associated with adverse remodeling and increased mortality in the short to medium term. Their long‐term prognostic impact is less well understood.
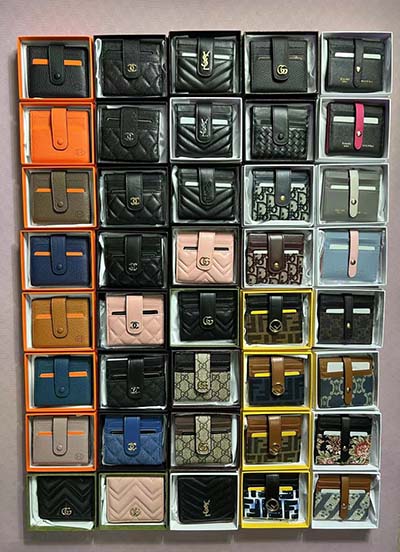
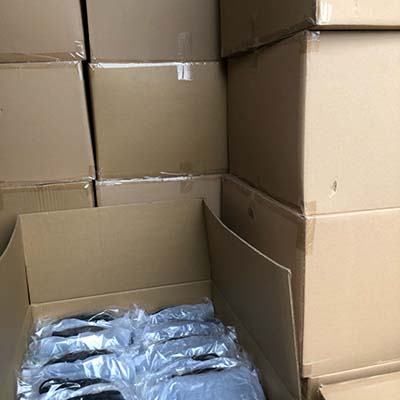
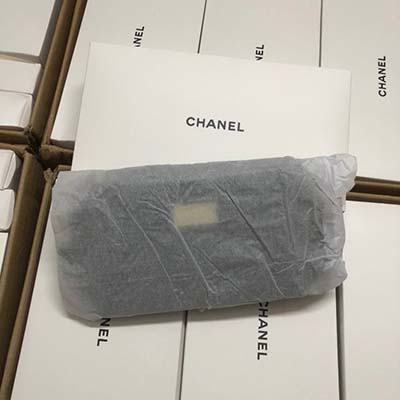
fake gucci hoodie cheap
Assessment of left ventricular systolic function has a central role in the evaluation of cardiac disease. Accurate assessment is essential to guide management and prognosis. Numerous echocardiographic techniques are used in the assessment, each . There were 52 patients (5.9%) with echocardiographic evidence of LV wall motion abnormality. Frequency of LV wall motion abnormality did not differ between patients with ESUS and those with small‐ or large‐artery strokes (5.7% versus 6.0%; P=0.9).Left Ventricular (LV) wall motion abnormalities (WMA) are an independent indicator of adverse cardiovascular events and death in patients with cardiovascular diseases such as myocardial infarction (MI), dyssynchrony and congenital heart disease (1, 2).
LBBB is known to cause septal wall motion abnormalities as well as to reduce systolic septal wall thickness. Thus, LBBB is a good non-ischaemic clinical model to evaluate the influence of wall thickness and wall motion on the homogeneity of tracer distribution in resting SPECT images.Abnormal ventricular wall motion is a strong clinical predictor of sudden, arrhythmic, cardiac death. Dispersion in repolarization is a prerequisite for the initiation of re-entrant arrhythmia. We hypothesize that regionally decreased wall motion is associated with heterogeneity of .The most frequent cause of regional wall motion abnormality is ischemic heart disease. Myocardial infarction may cause regional hypokinesia, akinesia or dyskinesia. The distribution of wall motion abnormalities should match the territory of a coronary artery.
Left ventricular hypertrophy is a thickening of the wall of the heart's main pumping chamber, called the left ventricle. This thickening may increase pressure within the heart. The condition can make it harder for the heart to pump blood.
Left ventricular wall motion abnormalities (LVWMAs) are commonly observed in a variety of medical conditions, including coronary artery disease, congestive heart failure, stress-induced cardiomyopathy, myocarditis, chronic renal disease, and stroke. 1–4 Their underlying disease mechanisms and their potential causative role for stroke remain . Echocardiographic evaluation of wall motion (WM) is a simple, well-validated method to assess segmental left ventricular (LV) function. 1,2 The presence of qualitative WM abnormalities has been demonstrated to be an independent predictor of cardiovascular events in groups of patients with myocardial infarction (MI), 3,4 unstable angina, 5 . Regional wall motion abnormalities (WMAs) after myocardial infarction are associated with adverse remodeling and increased mortality in the short to medium term. Their long‐term prognostic impact is less well understood.Assessment of left ventricular systolic function has a central role in the evaluation of cardiac disease. Accurate assessment is essential to guide management and prognosis. Numerous echocardiographic techniques are used in the assessment, each .
There were 52 patients (5.9%) with echocardiographic evidence of LV wall motion abnormality. Frequency of LV wall motion abnormality did not differ between patients with ESUS and those with small‐ or large‐artery strokes (5.7% versus 6.0%; P=0.9).Left Ventricular (LV) wall motion abnormalities (WMA) are an independent indicator of adverse cardiovascular events and death in patients with cardiovascular diseases such as myocardial infarction (MI), dyssynchrony and congenital heart disease (1, 2). LBBB is known to cause septal wall motion abnormalities as well as to reduce systolic septal wall thickness. Thus, LBBB is a good non-ischaemic clinical model to evaluate the influence of wall thickness and wall motion on the homogeneity of tracer distribution in resting SPECT images.
what is rwma in cardiology
regional wall motion abnormalities present
gucci backpack cheap for mens
Apron cam - Malta International Airport | A Warm Welcome to Malta - Malta .
lv wall motion abnormality|regional wall motion abnormalities present